Question
What are the principles and mechanics of the Video Head Impulse Test (vHIT), and how is the remote camera vHIT system advancing modern vestibular diagnostics?
Answer
The Video Head Impulse Test (vHIT) is a cornerstone in the objective evaluation of semicircular canal function and the integrity of the vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR). Developed to address the limitations of the traditional clinical Head Impulse Test (cHIT)—which detects only overt saccades and misses covert refixations—vHIT enables high-frequency, quantifiable assessment of VOR performance.
Among the most recent innovations, the remote camera Synapsys vHIT system by Inventis stands out for its ability to enhance patient comfort, minimize motion artifacts, and deliver exceptional diagnostic accuracy, thereby advancing the standard of care in modern vestibular testing.
1. Foundational Principles
From a physiological perspective, the vestibular system’s response is influenced by the mass, elasticity, and viscosity within the cupulo-endolymphatic system. The function of the vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR) varies across different frequency domains: low-frequency stimuli are more reliant on visual feedback, whereas high-frequency stimuli depend predominantly on vestibular input.
The Video Head Impulse Test (vHIT) is uniquely designed to evaluate high-frequency head movements, making it especially effective in identifying unilateral vestibular deficits and covert saccades that may go undetected by other means.
2. Why vHIT over cHIT?
The traditional clinical Head Impulse Test (cHIT), also known as the Halmagyi test, offers a binary result (positive/negative) and is limited to the detection of visible overt saccades. It cannot capture covert saccades, which occur during head motion and are imperceptible to the naked eye.
According to the literature, up to 14% of patients with vestibular pathology may exhibit covert saccades only, making instrumented evaluation essential. This diagnostic gap is precisely what vHIT was developed to fill.
3. The Mechanics of vHIT
The vHIT assesses the vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR) by calculating gain, the ratio of eye velocity to head velocity, and by identifying the presence of refixation saccades. To achieve accurate results, the test requires:
- Precise measurement of head and eye velocities
- High-speed infrared video recording
- Reliable calibration and real-time graphical analysis
4. Remote Camera vHIT: A Technological Leap
Unlike traditional goggle-based systems that rely on head-mounted accelerometers, the remote camera Synapsys vHIT system by Inventis utilizes advanced image-processing algorithms for both eye tracking and head pose estimation.
This innovation offers several key advantages:
- Elimination of slippage artifacts: Head-mounted systems are prone to motion between the goggles and the skull, often resulting in inaccurate readings. Remote camera systems avoid this issue entirely.
- Enhanced patient comfort: Particularly beneficial for pediatric patients, post-operative cases, or individuals with facial asymmetry.
- Greater examiner flexibility: The clinician can move the patient’s head freely without interfering with the device.
- Improved repeatability: Fewer head impulses are required—typically 5, compared to 15–20 with goggle-based systems—for reliable results.
- High-resolution accuracy: The Synapsys system offers exceptional tracking precision, with eye/head tracking accuracy of ±0.1°, gaze direction accuracy of ±0.4°, and VOR gain accuracy of ±0.08.
5. Illustrative Screen Outputs
To support clinical interpretation, remote camera vHIT systems provide comprehensive visual outputs, including:
- Canalograms displaying VOR gain across all six semicircular canals (Figure 1).
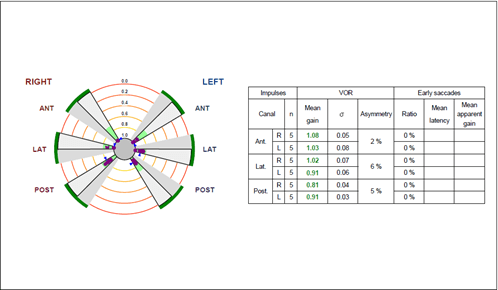
Figure 1
- Velocity graphs defining eye and head movements (Figure 2).
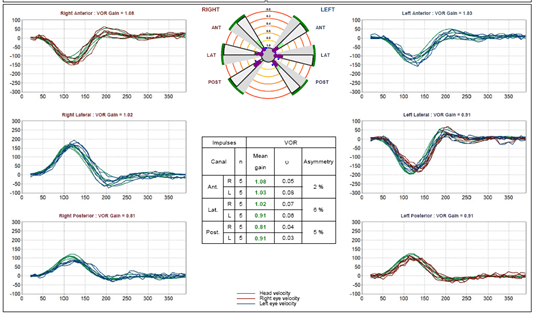
Figure 2
- Position traces and alignment graphs for identifying potential artifacts (Figure 3).
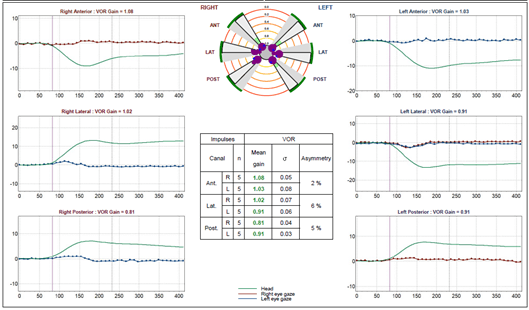
Figure 3
6. Case Illustration: When Remote Camera vHIT Made the Difference
Case Scenario:
A 31-year-old male presented with a 3-day history of severe spinning vertigo, characterized by spontaneous onset and worsened by head movements. The vertigo was continuous and accompanied by vomiting.
Examination Findings:
- Head Impulse Test: Abnormal on the left side
- Nystagmus: Unidirectional to the right, suppressed with visual fixation
- Skew Deviation: Absent
- Hearing Loss: None
- Unterberger’s Test: Rotation toward the left side
The patient underwent a video head impulse test, which revealed reduced gain in the left anterior and left lateral canals. Overt saccades were observed in the left lateral canal tracings (Figure 4).
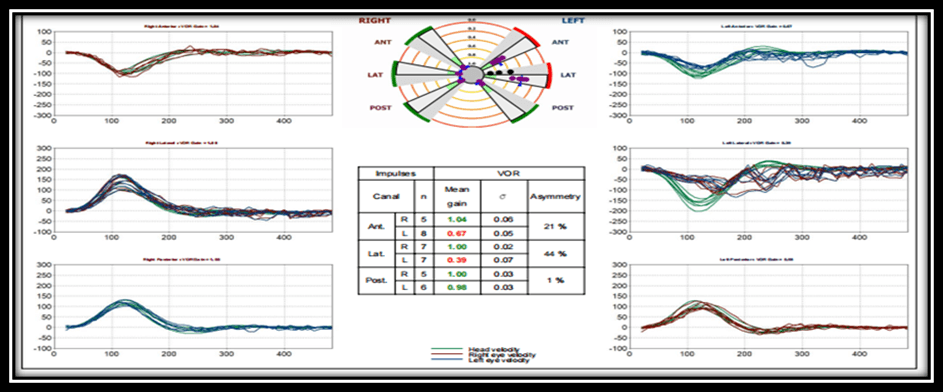
Figure 4
Final Diagnosis:
Left acute unilateral vestibulopathy involving the left superior branch of vestibular nerve.
Management:
The patient was started on targeted vestibular rehabilitation therapy, focusing on the left anterior and lateral canals, along with appropriate medical management.
Significance of vHIT:
The video head impulse test (vHIT) plays a critical role in cases like this by providing objective identification of canal-specific vestibular deficits. It enables precise localization of the lesion to the affected nerve and supports the development of individualized, targeted rehabilitation strategies.
7. Additional Clinical Applications of vHIT
- Subtyping Vestibular Neuritis: vHIT enables classification of superior, inferior, or ampullary involvement by analyzing canal-specific gain.
- Monitoring Ototoxicity or Surgical Outcomes: Useful in tracking vestibular function following gentamicin therapy, labyrinthectomy, or vestibular schwannoma resection.
- Acute Vertigo Triage: As part of the HINTS+ protocol, vHIT assists in differentiating peripheral from central causes of acute vestibular syndrome.
- Tracking Rehabilitation Progress: The presence of covert saccades may indicate compensation and help tailor the intensity and focus of vestibular rehabilitation.
- Vertical Canal Testing: vHIT effectively assesses the RALP and LARP planes, offering superior multidimensional analysis compared to traditional caloric testing.
8. Comparative Advantages Over Head-Mounted Systems
Feature | Head-Mounted Systems | Remote Camera vHIT |
Patient Comfort | Less comfortable (tight-fitting goggles) | Highly comfortable (no contact) |
Artifact from Slippage | Frequent | Absent |
Pediatric Use | Challenging | Feasible even in infants |
Required Maneuvers | 15–20 head impulses | 5 head impulses |
Examiner Maneuverability | Limited | Unrestricted |
Eye Tracking Technology | Accelerometer + camera | Pure image-based analysis |
Calibration Requirements | Laser-dependent | None |
Visual Field Obstruction | Present | None |
9. Conclusion: Shaping the Future of Vestibular Diagnostics
Remote camera vHIT systems represent a true paradigm shift in modern vestibular testing. Their contact-free design eliminates common sources of artifact, improves patient tolerance, and enables fast, objective, and reproducible measurements. By incorporating advanced gaze tracking, head pose estimation algorithms, and artifact-free performance, these systems provide a level of precision that not only enhances diagnostic accuracy but also supports targeted rehabilitation and the monitoring of recovery over time.
As the field of vestibular diagnostics continues to evolve, remote camera vHIT is emerging not merely as a diagnostic tool but as a transformative technology redefining how clinicians approach vertigo evaluation and neurotologic care.
Resources for More Information
- Discover our solutions for vestibular analysis on our website: https://www.inventis.it/en-na/solutions/balance-unique-solutions
- Check out the following courses published on AudiologyOnline:

