What is tinnitus?
Tinnitus, often described as ringing, buzzing or hissing sounds in the ears, is a symptom that can be related to almost every known hearing problem. Tinnitus can be temporary (acute) or permanent (chronic). It can also be constant or intermittent. Temporary tinnitus can be caused by exposure to loud sounds, middle or inner ear infections, and even wax on the eardrum. Because tinnitus can sometimes be treated medically, all patients who develop the symptom should first consult with an ear, nose and throat physician (otolaryngologist).
Tinnitus and hearing loss
Chronic tinnitus is usually associated with some degree of hearing loss. 90% of the patients who come to our Tinnitus Clinic have at least some hearing loss. Below are questions commonly asked by tinnitus patients:
Q: Does tinnitus cause hearing loss?
A: No. In fact, the reverse is true: whatever caused a person to have hearing loss (including noise exposure, infections, aging or genetic factors) is also responsible for the generation of tinnitus.
Q: Does tinnitus interfere with hearing?
A: No, tinnitus does not interfere with hearing, although it may affect one's attention span and concentration. On the other hand, tinnitus might seem louder if hearing loss increases (or if you wear ear plugs or ear muffs) because outside sounds will no longer reduce the perception of tinnitus.
Q: Does cutting the hearing nerve cure tinnitus?
A: Unfortunately, cutting the nerve does not relieve tinnitus often enough to recommend it as a treatment. It does, however, produce total deafness in the operated ear, may cause balance problems, and in some cases can make tinnitus worse.
How many people have chronic tinnitus?
According to Seidman & Jacobson,1 Approximately 40 million Americans have chronic tinnitus. For 10 million of these people, tinnitus can be a severely debilitating condition. However, for 30 million Americans with tinnitus, it is not bothersome. Tinnitus does not interfere with the enjoyment of life for the majority of people who experience it.
What can be done to help people who are bothered by chronic tinnitus?
I agree with Duckro et al2 who wrote: "As with chronic pain, the treatment of chronic tinnitus is more accurately described in terms of management rather than cure." The goal of tinnitus management is not necessarily to mask or remove the patient's physical perception of tinnitus sounds. Instead, we help patients learn to pay less attention to their tinnitus so that it bothers them less of the time. The realistic goal of an effective tinnitus management program is to help patients understand and gain control over their tinnitus, rather than it having control over them. Ultimately we hope to help patients progress to the point where tinnitus is no longer a negative factor in their lives. We want them to move from the "severely debilitated" group of tinnitus sufferers to the "not bothered by tinnitus" group and to enjoy their lives as much as possible.
There is usually no cure for chronic tinnitus that has been present for a year or more. One day, medical science will probably develop a way to eliminate the symptom. In the meantime, there are several effective management strategies that provide relief for most tinnitus patients.
Elements of an effective tinnitus management program
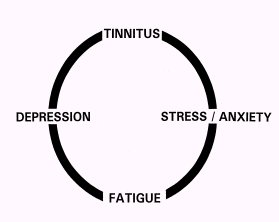
Tinnitus does not always start this cycle. Some patients experienced depression, insomnia, or anxiety before their tinnitus began. Tinnitus can, however, make each of these problems seem worse. Also, patients who continue to experience depression, insomnia, or anxiety report that these factors can cause their tinnitus to seem more severe. In these cases, effective treatment of depression, insomnia, and anxiety is necessary. A combination of medication and/or psychotherapy should reduce the severity of all of these conditions including tinnitus.
Things to Avoid
1) Harmful Sounds -- Wear ear plugs or ear muffs as protection against loud sounds such as gunfire, gas lawn mowers, leaf blowers, chain saws, circular saws, other power tools and heavy machinery. Exposure to loud sounds can make tinnitus worse and can also cause additional hearing loss.
2) Excessive use of alcohol, caffeine, or aspirin -- However, moderate use of these products is usually O.K.
3) False claims about tinnitus "cures" or herbal "remedies." These do not exist for most cases of chronic tinnitus.
Even though a true "cure" for most cases of chronic tinnitus is not yet available, patients can obtain relief from the symptom now with assistance from qualified and experienced clinicians.
References
1. Seidman MD, Jacobson GP. Update on tinnitus. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 1996 Jun;29(3):455-465.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov:80/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&list_uids=8743344&dopt=Abstract
2. Duckro PN, Pollard CA, Bray HD, Scheiter L. Comprehensive behavioral management of complex tinnitus: a case illustration. Biofeedback Self Regul 1984 Dec;9(4):459-469.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov:80/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&list_uids=6399462&dopt=Abstract
3. Folmer RL, Griest SE, Martin WH. Chronic tinnitus as phantom auditory pain. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2001 Apr;124(4):394-400.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov:80/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&list_uids=11283496&dopt=Abstract
4. Folmer RL, Griest SE. Tinnitus and insomnia. Am J Otolaryngol 2000 Sept-Oct;21(5):287-93.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov:80/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&list_uids=11032291&dopt=Abstract
5. Folmer RL, Griest SE, Meikle MB, Martin WH. Tinnitus severity, loudness, and depression. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 1999 Jul;121(1):48-51.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov:80/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&ist_uids=10388877&dopt=Abstract
For More Information
American Tinnitus Association
P.O. Box 5
Portland, OR 97207-0005
telephone: (800) 634-8978
email: tinnitus@ata.org
web: https://www.ata.org
OHSU Tinnitus Clinic
Mail Code NRC04
Oregon Health & Science University
3181 SW Sam Jackson Park Road
Portland, OR 97201-3098
telephone: (503) 494-7954
email: ohrc@ohsu.edu
web: https://www.ohsu.edu/ohrc/tinnitusclinic

